NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 3.2 (2025-26)
Sure! Here’s a polished and rewritten version of the paragraph with Mathify.in as the source:
Important Link:
📘 Mathify.in’s NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 – Coordinate Geometry (Exercise 3.2)
Mathify.in’s NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 3.2 are carefully prepared by subject experts to make your learning journey smoother and more effective. These solutions offer clear, step-by-step explanations to help you overcome any challenges while studying Coordinate Geometry. Designed to align seamlessly with the latest syllabus, they present all concepts in a reliable and easy-to-understand format.
📥 Download the Free PDF for NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Exercise 3.2 to boost your exam preparation and conceptual clarity.
🎯 Access the complete Class 9 Maths solutions now on Mathify.in

Solution:-
(i) The horizontal line used to determine the position of a point on the Cartesian plane is known as the x-axis. The vertical line used to identify the location of a point on the Cartesian plane is called the y-axis.
(ii) Each part of the place made by the X-axis and Y-axis is called the quadrants.
(iii) The point where the X-axis and the Y-axis meets is called as the origin ( 0 )


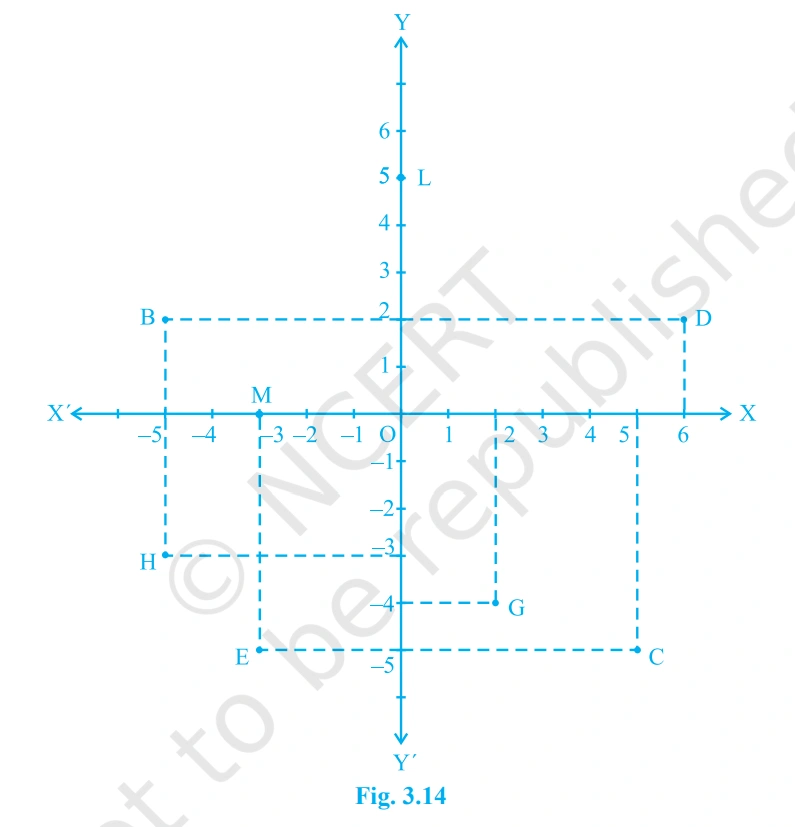
Solution:-
(i) The corrdinates of point B is the distance of point B from X-axis and Y-axis. So, the coordinates of point B are (- 5, 2).
(ii) The corrdinates of point (C) is the distance of point C from X-axis and Y-axis so, the corrdinates of point C are (5, -5).
(iii) The point that represents the coordinates ( – 3, -5) is E.
(iv) the point that represents the coordinates (2, -4) is G.
(v) The obscissa of point D is the distance of point D from the y-axis. So, the obscissa of point D is 6.
(vi) The ordinate of point H is the distance of point H from the X-axis, Therefore, the obscisa of point H is – 3.
(vii) The coordinates of point L in the above figure is the distance of point L from X-axis and Y-axis. So, the corrdinates of point L are (0, 5).
(viii) The corrdinates of point M in the above figure is the distance of point M from X-axis and Y-axis. So, the coordinates of point M are ( – 3, 0).
Conclusion
Exercise 3.2 of Chapter 3 in Class 9 Maths offers a solid introduction to the Cartesian coordinate system, laying the groundwork for spatial reasoning and geometric problem-solving. Through this exercise, students learn to plot points using coordinates, grasp the importance of the origin, and locate points within the four quadrants. These foundational skills are essential for mastering more advanced geometry concepts. Mathify.in provides clear, student-friendly explanations to ensure thorough understanding and confident application of these topics.