NCERT Class 7 Maths Ganita Prakash Chapter 3 A Peek Beyond The Point Solutions
3.1 The Need for Smaller Units
NCERT In-Text Questions (Pages 46 48)
Question: In the following figure, screws are placed above a scale. Measure them and write their length in the space provided.
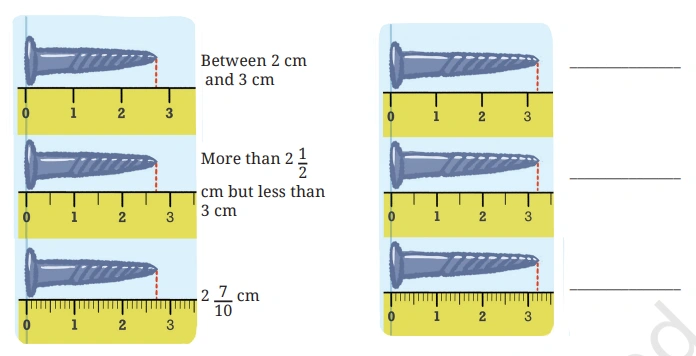
Solution:
Question: Which scale helped you measure the length of the screws accurately? Why?
Solution:
Question: Can you explain why the unit was divided into smaller parts to measure the screws?
Solution:
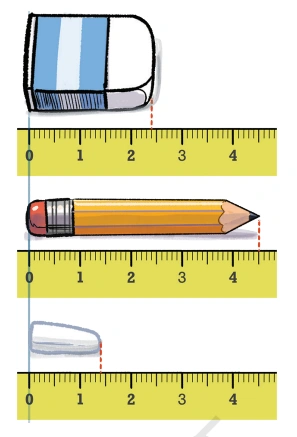
Question: Measure the following objects using a scale and write their measurements in centimeters (as shown earlier for the lengths of the screws): pen, sharpener, and any other object of your choice.
Solution:
Question: Write the measurements of the objects shown in the picture:
Solution:
3.2 A Tenth Part
NCERT In-Text Questions Pages (49-52)
Question: For the objects shown below, write their lengths in two ways and read them aloud. An example is given for the USB cable. (Note that the unit length used in each diagram is not the same). The length of the USB cable is 4 and 8/10 units or 48/10 units.
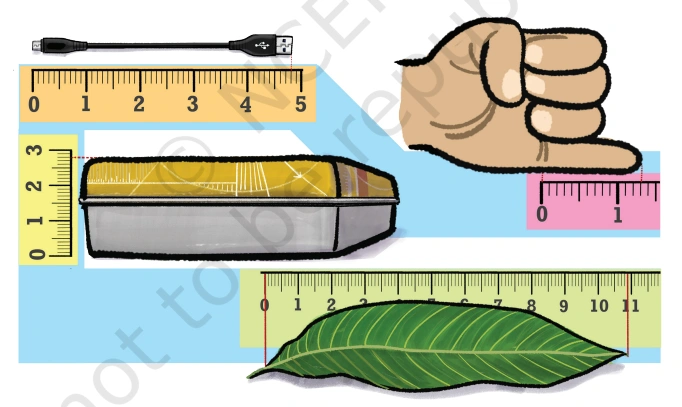
Solution:
Question: Arrange these lengths in increasing order:
(a) 9/10 (b) 1 7/10
(c) 130/10 (d) 13 1/10
(e) 10 5/10 (f) 7 6/10
(g) 6 7/10 (h) 4/10
Solution:-
Question: Arrange the following lengths in increasing order: 4 1/10, 4/10, 41/10, 41 1/10.
Solution:
Question: The lengths of the body parts of a honeybee are given. Find its total length.
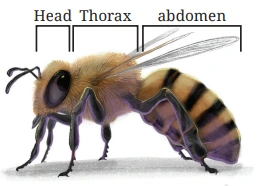
Head: 2 3/10 units
Thorax: 5 4/10 units
Abdomen: 7 5/10 units
Solution:-
Question: A Celestial Pearl Danio’s length is 2 4/10 cm, and the length of a Philippine Goby is 9/10 cm. What is the difference in their lengths?
Solution:
Question: How big are these fish compared to your finger?

Solution:
Question: Observe the given sequences of numbers. Identify the change after each term and extend the pattern:
(a) 4, 4 3/10 , 4 6/10 , , , ,
(b) 8 2/10 , 8 7/10 , 9 2/10 , , , ,
(c) 7 6/10 , 8 7/10 , , , ,
(d) 5 7/10 , 5 3/10 , , , ,
(e) 13 5/10 , 13, 12 5/10 , , , ,
(f) 11 5/10 , 10 4/10 , 9 3/10 , , , ,
Solution:
3.3 A Hundredth Part
NCERT In-Text Questions (Pages 54-56)
Question: How many one-hundredths make one-tenth? Can we also say that the length is 4 units and 45 one-hundredths?
Solution:
Question: Observe the figure below. Notice the markings and the corresponding lengths written in the boxes when measured from 0. Fill the lengths in the empty boxes.
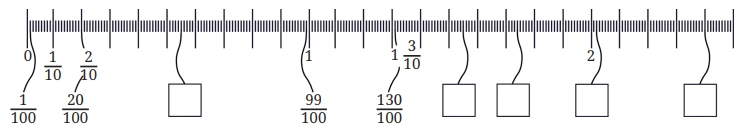
Solution:
Question: For the lengths shown below write the measurements and read out the measures in words.
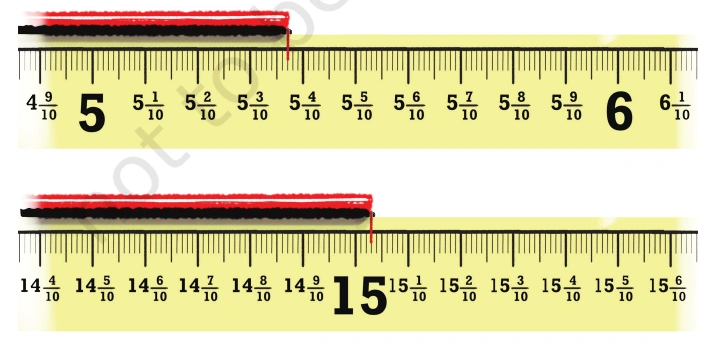
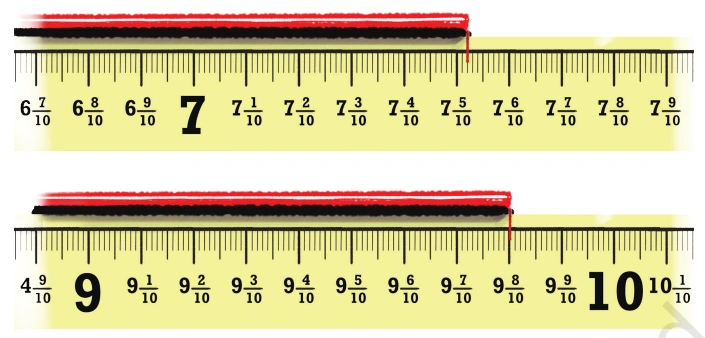
Solution:
Question: In each group, identify the longest and the shortest lengths. Mark each
length on the scale.
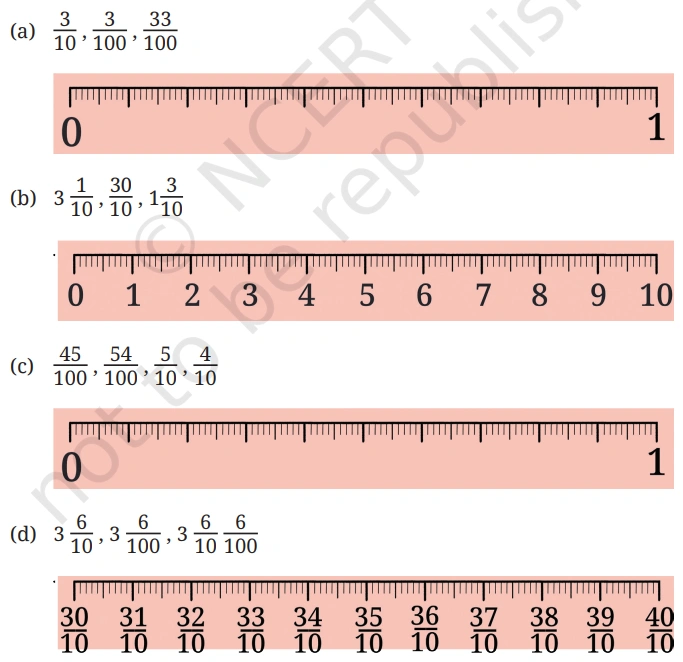
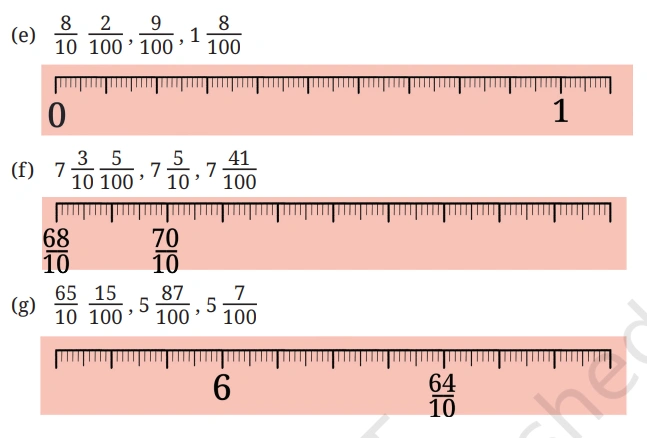
Solution:
Figure it Out Page 58
Question: Find the sums and differences:
(a) 3/10 + 3 4/100
(b) 9 5/10 7/100 + 2 1/10 3/100
(c) 15 6/10 4/100 + 14 3/10 6100
(d) 7 7/100 – 4 4/100
(e) 8 6/100 – 5 3/100
(f) 12 6/100 2/100 – 9/10 9/100
Solution:
3.4 Decimal Place Value
NCERT In-Text Questions Pages (61-64)
Question: We can ask similar questions about fractional parts:
(a) How many thousandths make one unit?
(b) How many thousandths make one tenth?
(c) How many thousandths make one hundredth?
(d) How many tenths make one ten?
(e) How many hundredths make one ten?
Solution:
Question: Make a few more questions of this kind and answer them
Solution:
Question: Make a place value table similar to the one above. Write each quantity in decimal form and in terms of place value, and read the number:
(a) 2 ones, 3 tenths and 5 hundredths
(b) 1 ten and 5 tenths
(c) 4 ones and 6 hundredths
(d) 1 hundred, 1 one and 1 hundredth
(e) 8/100 and 9/10
(f) 5/100
(g) 1/10
(h) 2 1/100 , 4 1/10 and 7 7/1000
Solution:-
Question: Write these quantities in decimal form:
(a) 234 hundredths,
(b) 105 tenths.
Solution:
3.5 Units of Measurement
Length Conversion
NCERT In-Text Questions Pages (65-66)
Question: Fill in the blanks below (mm <–> cm):
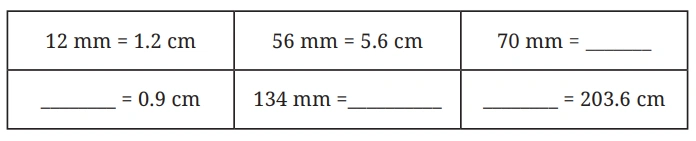
Solution:
Question: Fill in the blanks below (cm <–> m):
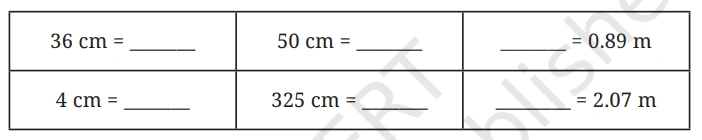
Solution:
Question: How many mm does 1 meter have?
Solution:
Weight Conversion
NCERT In-Text Questions Pages (67-68)
Question: Fill in the blanks below (g <–> kg).
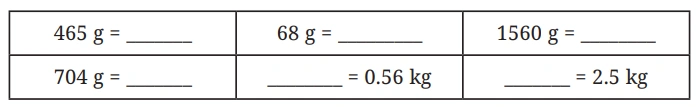
Solution:
Rupee-Paise Conversion
NCERT In-Text Questions Page 69
Question: Fill in the blanks below (rupee <–> paise)
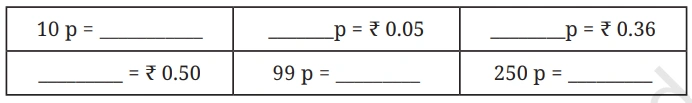
Solution:
3.6 Locating and Comparing Decimals
NCERT In-Text Questions Page 70
Question: Name all the divisions between 1 and 1.1 on the number line.
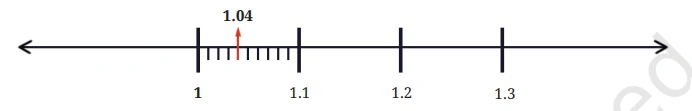
Solution:
Question: Identify and write the decimal numbers against the letters.
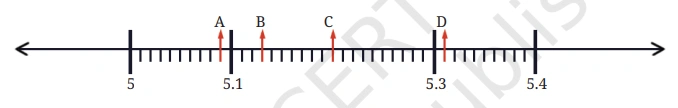
Solution:
There is Zero Dilemma
NCERT In-Text Questions Pages (71-73)
Question: Can you tell which of these (0.2, 0.02, and 0.002) is the smallest and which is the largest?
Solution:
Question: Which of these are the same: 4.5, 4.05, 0.405, 4.050, 4.50, 4.005, 04.50?
Solution:
Question: Identify the decimal number in the last number line in Figure (b) denoted by ‘?’.
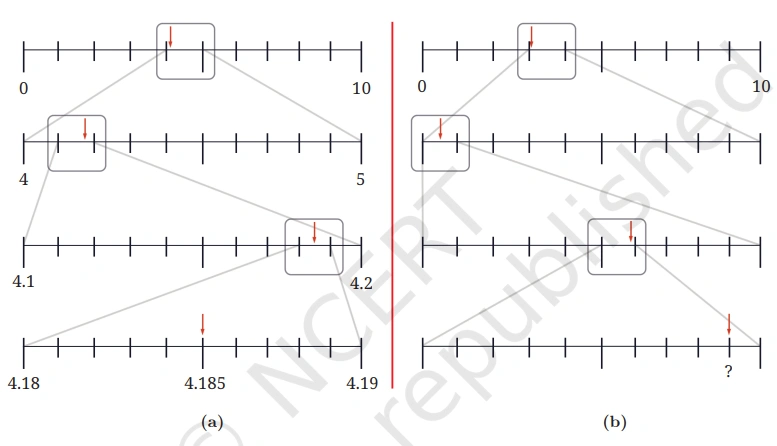
Solution:
Question: Make such number lines for the decimal numbers:
(a) 9.876
(b) 0.407.
Solution:
Question: In the number line shown below, what decimal numbers do the boxes labelled ‘a’, ‘b’, and ‘c’ denote?
The box with ‘b’ corresponds to the decimal number 7.5; are you able to see how? There are 5 units between 5 and 10, divided into 10 equal parts. Hence, every 2 divisions make a unit, and so every division is 1/2 unit. What numbers do ‘a’ and ‘c’ denote?
Solution:
Question: Using similar reasoning find out the decimal numbers in the boxes below.
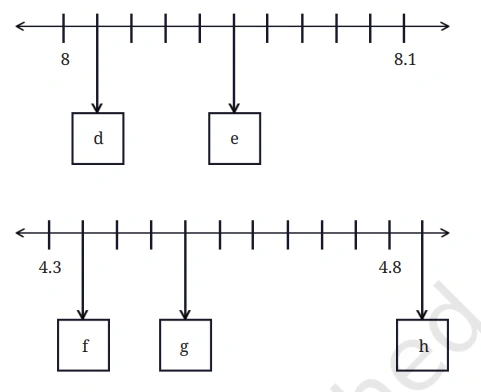
Solution:
Question: Which decimal number is greater?
(a) 1.23 or 1.32
(b) 3.81 or 13.800
(c) 1.009 or 1.090
Solution:
Closest Decimals
NCERT In-Text Questions Page 73
Question: Which of the above is closest to 1.09?
Solution:
Question: Which among these is closest to 4: 3.56, 3.65, 3.099?
Solution:
Question: Which among these is closest to 1: 0.8, 0.69, 1.08?
Solution:
Question: In each case below use the digits 4, 1, 8, 2, and 5 exactly once and try to make a decimal number as close as possible to 25.
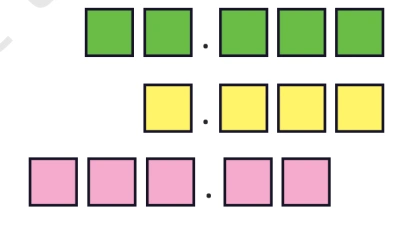
Solution:
3.7 Addition and Subtraction of Decimals
NCERT In-Text Questions Pages 75
Question: Write the detailed place value computation for 84.691 – 77.345, and its compact form.
Solution:
Figure it Out
Question 1: Find the sums
(a) 5.3 + 2.6 (b) 18 + 8.8
(c) 2.15 + 5.26 (d) 9.01 + 9.10
(e) 29.19 + 9.91 (f) 0.934 + 0.6
(g) 0.75 + 0.03 (h) 6.236 + 0.487
Solution:
Question 2: Find the differences
(a) 5.6 – 2.3 (b) 18 – 8.8
(c) 10.4 – 4.5 (d) 17 – 16.198
(e) 17 – 0.05 (f) 34.505 – 18.1
(g) 9.9 – 9.09 (h) 6.236 – 0.487
Solution:
Decimal Sequences
NCERT In-Text Questions Pages (75-76)
Question: Observe this sequence of decimal numbers and identify the change after each term.
4.4, 4.8. 5.2, 5.6, 6.0, …
We can see that 0.4 is being added to a term to get the next term. Continue this sequence and write the next 3 terms.
Solution:
Question: Similarly, identify the change and write the next 3 terms for each sequence given below. Try to do this computation mentally.
(a) 4.4, 4.45, 4.5, …
(b) 25.75, 26.25, 26.75, …
(c) 10.56, 10.67, 10.78, …
(d) 13.5, 16, 18.5, …
(e) 8.5, 9.4, 10.3, …
(f) 5, 4.95, 4.90, …
(g) 12.45, 11.95, 11.45, …
(h) 36.5, 33, 29.5, …
Solution:
Question: Make your own sequences and challenge your classmates to extend the pattern.
Solution:
Estimating Sums and Differences
NCERT In-Text Questions Pages 76
Sonu has observed sums and differences of decimal numbers and says, “If we add two decimal numbers, then the sum will always be greater than the sum of their whole number parts. Also, the sum will always be less than 2 more than the sum of their whole number parts.”
Let us use an example to understand what his claim means: If the two numbers to be added are 25.936 and 8.202, the claim is that their sum will be greater than 25 + 8 (whole number parts) and will be less than 25 + 1 + 8 + 1.
Quesion: What do you think about this claim? Verify if this is true for these numbers. Will it work for any 2 decimal numbers?
Solution:
Question: What about for the sum of 25.93603259 and 8.202?
Solution:
Question: Similarly, come up with a way to narrow down the range of whole numbers within which the difference of two decimal numbers will lie.
Solution:
3.8 More on the Decimal
System Deceptive Decimal Notation
NCERT In-Text Questions Pages 78
Question: Where else can we see such ‘non-decimals’ with a decimal-like notation?
Solution:
Figure it Out Page 78-79
Question 1: Convert the following fractions into decimals:
(a) 5/100 (b) 16/1000 (c) 12/10 (d) 254/1000
Solution:
Question 2: Convert the following decimals into a sum of tenths, hundredths and thousandths:
(a) 0.34 (b) 1.02 (c) 0.8 (d) 0.362
Solution:
Question 3. What decimal number does each letter represent in the number line below?
Solution:
Question 4. Arrange the following quantities in descending order:
(a) 11.01, 1.011, 1.101, 11.10, 1.01
(b) 2.567, 2.675, 2.768, 2.499, 2.698
(c) 4.678 g, 4.595 g, 4.600 g, 4.656 g, 4.666 g
(d) 33.13 m, 33.31 m, 33.133 m, 33.331 m, 33.313 m
Solution:
Question 5: Using the digits 1, 4, 0, 8, and 6 make:
(a) the decimal number closest to 30
(b) the smallest possible decimal number between 100 and 1000.
Solution:
Question 6: Will a decimal number with more digits be greater than a decimal number with fewer digits?
Solution:
Question 7: Mahi purchases 0.25 kg of beans, 0.3 kg of carrots, 0.5 kg of potatoes, 0.2 kg of capsicums, and 0.05 kg of ginger. Calculate the total weight of the items she bought.
Solution:
Question 8. Pinto supplies 3.79 L, 4.2 L, and 4.25 L of milk to a milk dairy in the first three days. In 6 days, he supplies 25 litres of milk. Find the total quantity of milk supplied to the dairy in the last three days.
Solution:
Question 9. Tinku weighed 35.75 kg in January and 34.50 kg in February. Has he gained or lost weight? How much is the change?
Solution:
Question 10. Extend the pattern: 5.5, 6.4, 6.39, 7.29, 7.28, 6.18, 6.17, , _
Solution:
Question 11. How many millimeters make 1 kilometer?
Solution:
Question 12: Indian Railways offers optional travel insurance for passengers who book e-tickets. It costs 45 paise per passenger. If 1 lakh people opt for insurance in a day, what is the total insurance fee paid?
Solution:
Question 13: Which is greater?
(a) 10/1000 or 1/10 ?
(b) One-hundredth or 90 thousandths?
(c) One-thousandth or 90 hundredths?
Solution:
Question 14: Write the decimal forms of the quantities mentioned (an example is given):
(a) 87 ones, 5 tenths and 60 hundredths = 88.10
(b) 12 tens and 12 tenths
(c) 10 tens, 10 ones, 10 tenths, and 10 hundredths
(d) 25 tens, 25 ones, 25 tenths, and 25 hundredths
Solution:
Question 15: Using each digit 0 – 9 not more than once, fill the boxes below so that the sum is closest to 10.5:
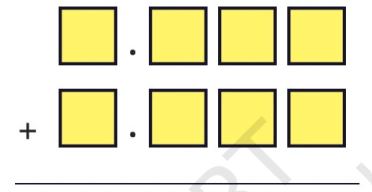
Solution:
Question 16: Write the following fractions in decimal form:
(a) 1/2
(b) 3/2
(c) 1/4
(d) 3/4
(e) 1/5
(f) 4/5
Solution: